How Does a Surrogate Mother Get Pregnant
Surrogacy, which is a process where a woman carries a child for another individual or couple, has become an increasingly popular option for those struggling with infertility or other medical conditions. But how does a surrogate mother actually become pregnant?
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the process of surrogacy, explaining the various methods and procedures involved in helping a surrogate mother conceive. By understanding the steps and techniques used, you can gain valuable insights into the remarkable journey of surrogacy.
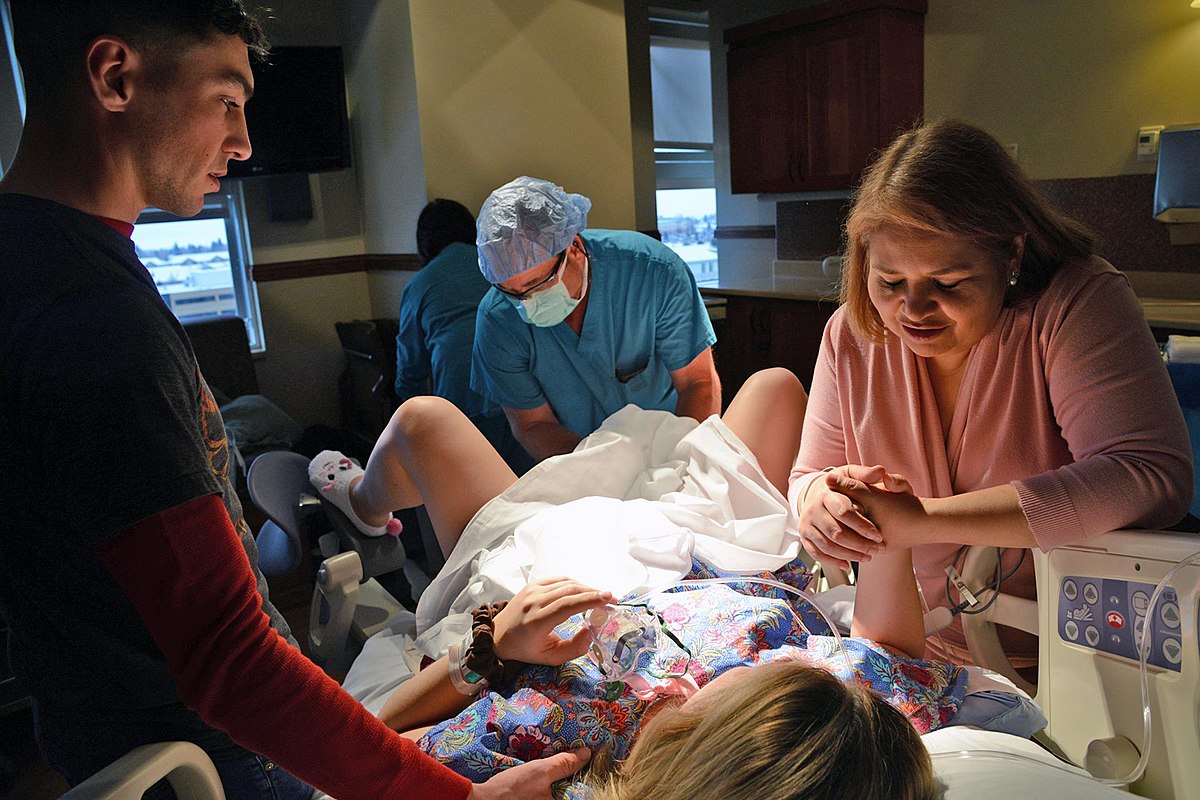

1. Traditional Surrogacy
In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate mother’s own eggs are used for conception. Here’s an overview of the process:
a. Ovulation Induction: The surrogate mother undergoes ovulation induction, which involves taking fertility medications to stimulate the production of multiple eggs.
b. Insemination: Once the eggs are mature, the intended father’s sperm or donor sperm is artificially inseminated into the surrogate mother’s uterus using a catheter. This is typically done during the surrogate’s fertile window.
c. Pregnancy Confirmation: Approximately two weeks after insemination, a pregnancy test is conducted to determine if the surrogate mother has successfully conceived.
2. Gestational Surrogacy
Gestational surrogacy is the more common form of surrogacy, where the surrogate mother carries an embryo created from the intended parents’ or donors’ genetic material. Let’s explore the process:
a. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): The intended mother or an egg donor undergoes IVF, where eggs are retrieved and fertilized with the intended father’s sperm or donor sperm in a laboratory setting.
b. Embryo Transfer: After fertilization, the resulting embryos are carefully monitored and allowed to develop for a few days. One or more embryos are then transferred into the surrogate mother’s uterus through a thin catheter.
c. Pregnancy Confirmation: Approximately two weeks after the embryo transfer, a pregnancy test is conducted to determine if the surrogate mother has successfully conceived.
3. Medical Screening and Support
Throughout the surrogacy process, both the surrogate mother and intended parents undergo extensive medical screening to ensure their suitability for the journey. This includes physical examinations, hormone level evaluations, and infectious disease screenings.
Additionally, the surrogate mother receives ongoing medical support and monitoring throughout the pregnancy, ensuring the well-being of both her and the developing fetus.
4. Legal and Emotional Considerations
Surrogacy arrangements involve legal contracts outlining the rights, responsibilities, and expectations of all parties involved. These contracts address issues such as parental rights, financial arrangements, and medical decision-making.
Emotional support is also crucial, as surrogacy can be an emotionally challenging journey for all parties. Counseling and support groups can provide guidance and assistance in navigating the emotional aspects of surrogacy.
Surrogacy and the Process of Becoming Pregnant as a Surrogate Mother:
1. Matching Process
Before the surrogate mother becomes pregnant, there is a matching process that takes place. Surrogacy agencies or intended parents may review profiles of potential surrogate mothers and select someone who aligns with their preferences and values. The matching process involves considerations such as medical history, personal background, and compatibility between the surrogate and intended parents.
2. Embryo Quality and Transfer
In gestational surrogacy, the quality of the embryos plays a crucial role in the success of the pregnancy. Embryos that have a higher chance of implantation and successful development are typically selected for transfer. Embryo quality is determined by factors such as the number of cells, symmetry, and the absence of genetic abnormalities.
3. Multiple Embryo Transfers
In some cases, multiple embryos may be transferred into the surrogate mother’s uterus to increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. However, this also raises the possibility of multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets. The decision to transfer multiple embryos is usually made after considering various factors, including the age of the intended mother or egg donor and the quality of the embryos.
4. Surrogate Mother’s Role
Throughout the pregnancy, the surrogate mother plays a vital role in ensuring the well-being of the developing fetus. She follows a comprehensive prenatal care plan, which includes regular check-ups, ultrasounds, and medical consultations. The surrogate mother also adheres to specific guidelines regarding nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle choices to optimize the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
5. Birth and Post-Delivery Process
Once the surrogate mother reaches full term, she goes into labor and delivers the baby. In most cases, the intended parents are present during the birth, providing emotional support and forming the initial bond with their child. After the birth, legal processes, including the establishment of parental rights, are initiated to ensure a smooth transition of custody from the surrogate mother to the intended parents.
6. Compensation for Surrogate Mothers
Surrogate mothers are typically compensated for their time, effort, and commitment throughout the surrogacy journey. The cost of surrogacy varies depending on factors such as the location, the specific surrogacy arrangement, and any additional expenses or requirements. It is important to note that surrogacy laws and regulations regarding compensation vary between countries and jurisdictions.
7. Emotional Considerations and Support
Embarking on the journey of surrogacy can be emotionally complex for both surrogate mothers and intended parents. It is crucial for all parties involved to have access to emotional support, whether through counseling services, support groups, or dedicated surrogacy agencies that provide guidance and assistance throughout the process.
Factors Affecting Surrogate Compensation
The amount of compensation a surrogate mother receives can vary depending on several factors, including:
a. Geographic Location: Compensation rates can vary significantly based on the region or country where the surrogacy takes place. For example, surrogate compensation may differ between the United States, Canada, or other countries due to variations in local laws, medical costs, and living expenses.
b. Agency or Independent Surrogacy: Working with a surrogacy agency often involves additional fees, which can impact the overall compensation. Independent surrogacy arrangements, where the surrogate and intended parents connect directly, may have different financial agreements.
c. Surrogate’s Experience: Surrogates with previous successful surrogacy journeys or those who have specific qualifications or characteristics desired by intended parents may command higher compensation.
d. Gestational or Traditional Surrogacy: Compensation rates can differ between gestational surrogacy (where the surrogate does not use her own eggs) and traditional surrogacy (where the surrogate is genetically related to the child she carries).
Components of Surrogate Compensation
Surrogate compensation typically consists of multiple components, which may include:
a. Base Compensation: This is the primary fee paid to the surrogate for her commitment and time involved in the surrogacy process. Base compensation varies and is typically negotiated between the surrogate and the intended parents or agency.
b. Pregnancy-Related Expenses: Surrogate mothers are typically reimbursed for medical and pregnancy-related expenses, such as prenatal care, maternity clothing, medications, and travel expenses for medical appointments.
c. Insurance and Legal Expenses: Intended parents usually cover the cost of health insurance for the surrogate, ensuring comprehensive coverage throughout the pregnancy. Legal expenses associated with drafting and reviewing contracts may also be covered.
d. Additional Compensation: Surrogates may receive additional compensation for specific circumstances or demands, such as carrying multiples (twins or triplets) or undergoing invasive medical procedures.
How much does Surrogacy make: Examples of the cost of Surrogacy
It is important to note that the surrogate cost of surrogacy can vary widely depending on the factors mentioned above. Here are some illustrative examples:
a. In the United States, surrogate compensation can range from $30,000 to $50,000 or more, excluding additional expenses and benefits.
b. In Canada, where commercial surrogacy is prohibited, surrogates may receive reimbursement for reasonable expenses but no additional compensation beyond that.
c. In other countries, surrogate compensation may fall within a different range, reflecting the local economic factors and healthcare costs.
Non-Financial Rewards
While financial compensation is an important consideration, it’s essential to acknowledge the non-financial rewards of surrogacy. Many surrogates find immense fulfillment in helping intended parents realize their dreams of having a child. The emotional satisfaction, the bonds formed, and the positive impact on all parties involved are immeasurable.
Here are 10 Frequently Asked Questions on Surrogacy, Along With Their Answers:
1. Q: What is surrogacy?
A: Surrogacy is a legal arrangement where a woman, known as the surrogate mother, carries and gives birth to a child on behalf of another person or couple, known as the intended parents. The surrogate mother carries the pregnancy with the intention of giving the child to the intended parents after birth.
2. Q: How does surrogacy work?
A: Surrogacy typically involves the use of in vitro fertilization (IVF) techniques. The intended parents or a donor provide eggs and sperm, which are fertilized in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the surrogate mother’s uterus for implantation and gestation.
3. Q: What are the different types of surrogacy?
A: There are two main types of surrogacy: traditional surrogacy and gestational surrogacy. In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate mother’s own eggs are used, making her genetically related to the child. In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate mother carries an embryo created using the eggs and sperm of the intended parents or donors, making her genetically unrelated to the child.
4. Q: How are surrogate mothers selected?
A: The selection of surrogate mothers can be done through surrogacy agencies or independently. Surrogacy agencies typically have a thorough screening process that includes medical and psychological evaluations, background checks, and matching the surrogate’s preferences with the intended parents. Independent surrogacy arrangements involve the intended parents and surrogate mother connecting directly to establish a mutually agreeable relationship.
5. Q: What are the legal aspects of surrogacy?
A: The legal aspects of surrogacy vary depending on the jurisdiction. It is crucial to consult with legal professionals who specialize in reproductive law to understand the specific laws and regulations governing surrogacy in the relevant jurisdiction. Legal agreements, including contracts outlining the rights and responsibilities of all parties involved, are typically established to protect the rights of the surrogate mother and intended parents.
6. Q: How much does surrogacy cost?
A: The cost of surrogacy varies depending on several factors, including the location, type of surrogacy, medical expenses, legal fees, agency fees (if applicable), and compensation for the surrogate mother. It is essential to consult with surrogacy professionals to obtain a detailed cost breakdown based on individual circumstances.
7. Q: Are surrogate mothers paid for their services?
A: Surrogate mothers are typically compensated for their time, effort, and the physical and emotional commitment involved in the surrogacy process. The cost of surrogacy varies and is determined by factors such as the location, the type of surrogacy, and any additional expenses or requirements.
8. Q: Is surrogacy legal in all countries?
A: Surrogacy laws vary from country to country and even within different states or provinces. Some countries have specific legislation that allows and regulates surrogacy, while others may have restrictions or prohibit commercial surrogacy altogether. It is essential to research and understands the surrogacy laws and regulations in the intended location before proceeding with the process.
9. Q: Can same-sex couples or single individuals pursue surrogacy?
A: Yes, same-sex couples and single individuals can pursue surrogacy to build their families. Surrogacy provides an opportunity for individuals or couples who may not be able to conceive or carry a child on their own to become parents.
10. Q: What are the emotional considerations involved in surrogacy?
A: Surrogacy is a complex and emotionally charged journey for all parties involved. Open and honest communication, emotional support, and counseling services can be beneficial for both the intended parents and the surrogate mother throughout the surrogacy process. It is crucial to establish a strong and supportive relationship, maintain open lines of communication, and ensure that everyone’s emotional well-being is prioritized.
Conclusion
Surrogacy is a remarkable process that enables individuals and couples to fulfill their dreams of parenthood. Whether through traditional surrogacy, where the surrogate mother’s eggs are used, or gestational surrogacy, involving the transfer of embryos, the journey of surrogacy is a carefully orchestrated process that combines medical, legal, and emotional elements.
By understanding the steps involved, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable individuals who choose to become surrogate mothers and help bring the gift of life to others.