Heavy Bleeding During Pregnancy: Common Triggers and Solutions
Pregnancy is an exciting journey, but it can also raise concerns when unexpected issues arise. One such concern is bleeding during pregnancy. While some bleeding may be normal, heavy bleeding can be distressing.
In this article, we’ll consider heavy bleeding during pregnancy, how much bleeding is considered normal in early pregnancy, the possible causes of pregnancy-related bleeding, and specific types of bleeding like nosebleeds and gum bleeding. We’ll also address whether bleeding during pregnancy is normal or requires medical attention.

Heavy Bleeding During Pregnancy
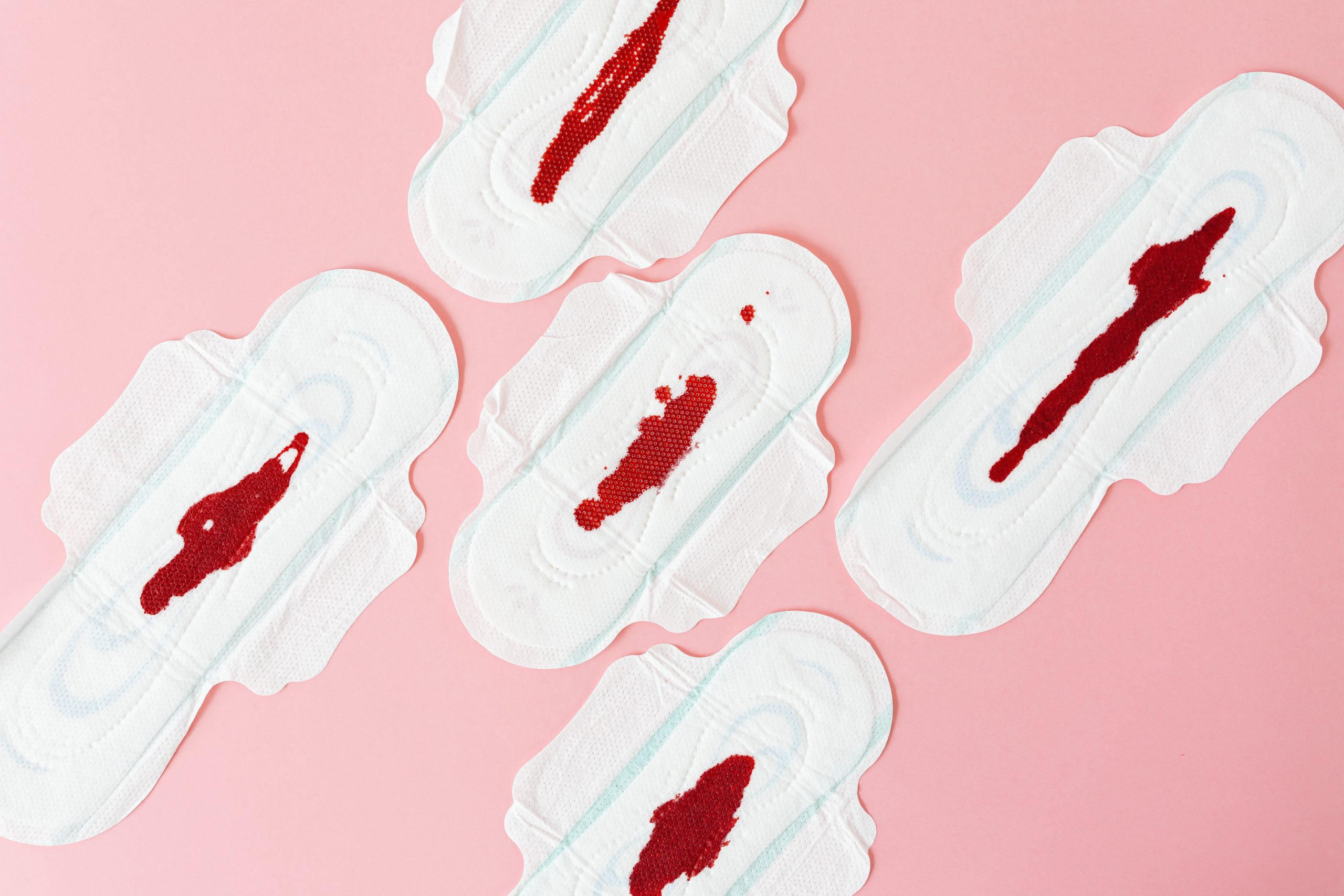
Experiencing heavy bleeding during pregnancy can be alarming, and it’s essential to understand when to be concerned. Heavy bleeding involves significant amounts of blood, soaking through a pad or tampon quickly. It may be accompanied by severe cramps, pain, or the passing of tissue. Approximately 20% of pregnant women experience bleeding at some point during their pregnancy, but heavy bleeding is less common and may require immediate medical attention.
How Much Bleeding is Normal in Early Pregnancy
In early pregnancy, some women may experience light spotting or bleeding, known as implantation bleeding. This usually occurs around the time of their expected period and can affect around 25% of pregnancies. Implantation bleeding is generally light and poses no threat to the pregnancy.
Why Bleeding During Pregnancy – Causes
Approximately 15% of pregnant women experience bleeding during their first trimester. Several factors can contribute to bleeding during pregnancy. Below are some of the causes of bleeding during pregnancy:
- Implantation: As the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining, mild spotting or bleeding may occur.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels during pregnancy can lead to minor bleeding.
- Miscarriage: Heavy bleeding, cramping, and passing tissue may indicate a miscarriage. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect a miscarriage.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: In rare cases, the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, causing heavy bleeding and severe pain. This requires immediate medical attention.
- Infections: Infections of the cervix or vagina can cause bleeding during pregnancy.
- Placental Problems: Issues with the placenta, such as placenta previa or placental abruption, can lead to bleeding.
Symptoms That Come Along With Heavy Bleeding During Pregnancy
Aside from heavy bleeding, other symptoms may accompany the condition, such as:
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping.
- Passing tissue or clots from the vagina.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness due to blood loss.
Nose Bleeding During Pregnancy
Causes of Nose Bleeding During Pregnancy:
1. Hormonal Changes: During pregnancy, increased estrogen levels can lead to increased blood flow and dilated blood vessels, including those in the nasal passages. This makes the delicate blood vessels more prone to rupturing, resulting in nosebleeds. Approximately 30% of pregnant women may experience nosebleeds due to hormonal changes and increased blood flow.
2, Dry Air and Nasal Congestion: Many pregnant women experience nasal congestion due to hormonal changes. Dry air, common in heated indoor environments or dry climates, can further dry out the nasal passages, making them more susceptible to irritation and nosebleeds.
3. Nasal Friction or Nose Picking: The increased sensitivity of blood vessels during pregnancy means that even slight friction or irritation in the nose, such as frequent nose picking, can trigger a nosebleed.
4. Increased Blood Volume: Pregnancy leads to an increased volume of blood circulating in the body. This can cause the blood vessels in the nose to become more sensitive, making them more likely to bleed.
5. Infections and Irritants: Infections of the nasal passages or exposure to irritants like smoke or dust can lead to inflammation and irritation, potentially resulting in nosebleeds.
6. Nasal Allergies: Allergies, common during pregnancy, can cause nasal congestion and inflammation, increasing the risk of nosebleeds.
7. High Blood Pressure: In some cases, elevated blood pressure during pregnancy can contribute to nosebleeds.
8. Dry Mouth or Dehydration: A dry mouth or dehydration can affect the nasal passages’ moisture levels, making the blood vessels more susceptible to rupture.
9. Side Effects of Medications: Certain medications, including blood thinners or decongestants, can increase the likelihood of nosebleeds.
10. Underlying Medical Conditions: Pregnant women with pre-existing conditions like blood clotting disorders may be more prone to nosebleeds.
Managing Nose Bleeding During Pregnancy:
1. Stay Calm and Upright: If you experience a nosebleed, sit up straight and stay calm. This helps reduce blood pressure in the nose and may help slow down the bleeding.
2. Lean Forward and Pinch Your Nose: Gently lean your head slightly forward to prevent blood from flowing down your throat. Then, use your thumb and index finger to pinch the soft part of your nose, just below the bridge. Hold the pinch for 5-10 minutes while breathing through your mouth. This helps apply pressure to the bleeding vessels and can stop the bleeding.
3. Apply a Cold Compress: Placing a cold compress or ice pack on the bridge of your nose can help constrict blood vessels and reduce bleeding.
4. Avoid Blowing Your Nose: After a nosebleed, avoid blowing your nose immediately, as it can cause further irritation and bleeding.
Preventing Nose Bleeding During Pregnancy:
5. Use a Humidifier: Keeping the air in your living spaces moist can help prevent your nasal passages from drying out, reducing the risk of nosebleeds.
6. Nasal Saline Spray: Using a saline nasal spray can help keep your nasal passages moisturized and prevent dryness and irritation.
7. Avoid Nose Picking: Be gentle with your nose and avoid picking it, as this can cause unnecessary friction and increase the chances of nosebleeds.
8. Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps keep your body hydrated, which can also help maintain moist nasal passages.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Nosebleed During Pregnancy
While nosebleeds during pregnancy are usually benign, there are certain situations when you should seek medical attention:
- If nosebleeds are frequent, severe, or last longer than 20 minutes.
- If you experience excessive blood loss or feel weak and dizzy during a nosebleed.
- If you have a history of bleeding disorders or take blood-thinning medications.
Gum Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes, Dental Care, and Precautions
Causes of Gum Bleeding During Pregnancy:
1. Hormonal Changes: Similar to nosebleeds, hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to bleeding. Increased estrogen and progesterone levels can lead to inflammation of the gums, a condition known as pregnancy gingivitis.
2. Plaque Buildup: Hormonal changes can also affect how your body responds to plaque. Pregnant women may be more susceptible to plaque buildup, which can irritate the gums and cause bleeding.
3. Increased Blood Volume: During pregnancy, your body produces more blood to support the growing baby. This increased blood volume can cause the tiny blood vessels in your gums to become more sensitive, leading to bleeding even with minor irritation.
4. Weakened Immune System: Pregnancy can temporarily weaken the immune system to prevent the body from rejecting the developing fetus. This weakened immunity may make the gums more susceptible to inflammation and infection, further increasing the likelihood of gum bleeding.
5. Poor Nutrition: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients during pregnancy, such as vitamin C and vitamin K, can affect the health of your gums. These vitamins are crucial for maintaining healthy gum tissue and promoting proper blood clotting.
6. Pregnancy Tumors (Pyogenic Granulomas): Some pregnant women may develop growths on their gums called pregnancy tumors or pyogenic granulomas. These tumors are non-cancerous and usually harmless, but they can cause bleeding and discomfort in the mouth.
7. Stress: Pregnancy can be a stressful time, and stress can affect your oral health. High-stress levels can lead to teeth grinding (bruxism) and clenching, which can irritate the gums and cause bleeding.
8. Gingivitis Prior to Pregnancy: If you had gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) before becoming pregnant, the hormonal changes during pregnancy can exacerbate the condition, leading to increased gum bleeding.
9. Medications: Some medications taken during pregnancy may have side effects that affect gum health and increase the risk of bleeding.
10. Existing Dental Issues: Any pre-existing dental problems, such as tooth decay or gum disease, can worsen during pregnancy and contribute to gum bleeding.
11. Smoking and Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products during pregnancy can aggravate gum health and lead to bleeding.
12. Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene practices, such as irregular brushing and flossing, can allow plaque to build up on teeth and gums, leading to inflammation and bleeding.
Dental Care and Precautions:
1. Regular Dental Check-ups: It’s essential to continue regular dental check-ups during pregnancy. Inform your dentist that you are pregnant so they can tailor treatments and offer appropriate advice.
2. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque from between your teeth and along the gumline.
3. Use a Mild Mouthwash: Rinse your mouth with a mild, alcohol-free mouthwash to help reduce bacteria and maintain oral hygiene.
4. Be Gentle While Brushing: Brush your teeth gently to avoid irritating the sensitive gums.
5. Eat a Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet, rich in vitamins and minerals, supports good oral health during pregnancy.
6. When to Seek Dental Advice: If you experience persistent or severe gum bleeding, or if you notice changes in your oral health during pregnancy, consult your dentist. Early intervention can help prevent further complications and ensure a healthy smile throughout your pregnancy.
Is it Normal to Bleed During Pregnancy?
While light spotting or bleeding during early pregnancy can be normal, heavy bleeding is not typical and requires attention. Any bleeding during pregnancy should be reported to a medical practitioner for evaluation. It’s always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical advice.
What are The Treatment Options for Heavy Bleeding During Pregnancy?
The treatment for heavy bleeding during pregnancy depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, such as miscarriages or ectopic pregnancies, medical intervention or surgery may be necessary. For less severe cases, your doctor may recommend bed rest and close monitoring to ensure the bleeding subsides.
RELATED ARTICLE: How to Stop Bleeding During Pregnancy: Practical Tips for Expectant Mothers